Following our participation in the Blue Med Days in Marseille, it became evident that biofuels are getting increased attention in the maritime sector. With discussions around this topic intensifying, it’s clear that biofuels can potentially play an important role in helping shipowners adress the growing environmental regulatory demands. This article offers a comprehensive examination of biofuels, detailing their potential, benefits, and the challenges they pose within the maritime landscape.
According to the lastest report from the European Maritime Safety Agency, despite existing barriers, the uptake of biofuels is expected to increase, as it is the only readily available option at the industry to start its decarbonisation.
What is a biofuel?
Biofuels are renewable energy sources derived from organic matter, usually plants or algae. These fuels serve as alternatives to conventional fossil fuels like petrol and diesel. Biofuels can be broadly classified into, liquid biofuels and gaseous biofuels.
The versatility of biofuels allows them to be produced from various organic materials, including food crops, non-food crops, waste materials, and even specific algae.
Here are a few of the existing biofuels:
- Biodiesel: Made from vegetable oils.
- Renewable Diesel (HVO): Hydroprocessed vegetable oil.
- Methanol and Ethanol: Alcohol-based fuels typically derived from plant matter or biomass.
- Butanol: Produced through fermentation of biomass.
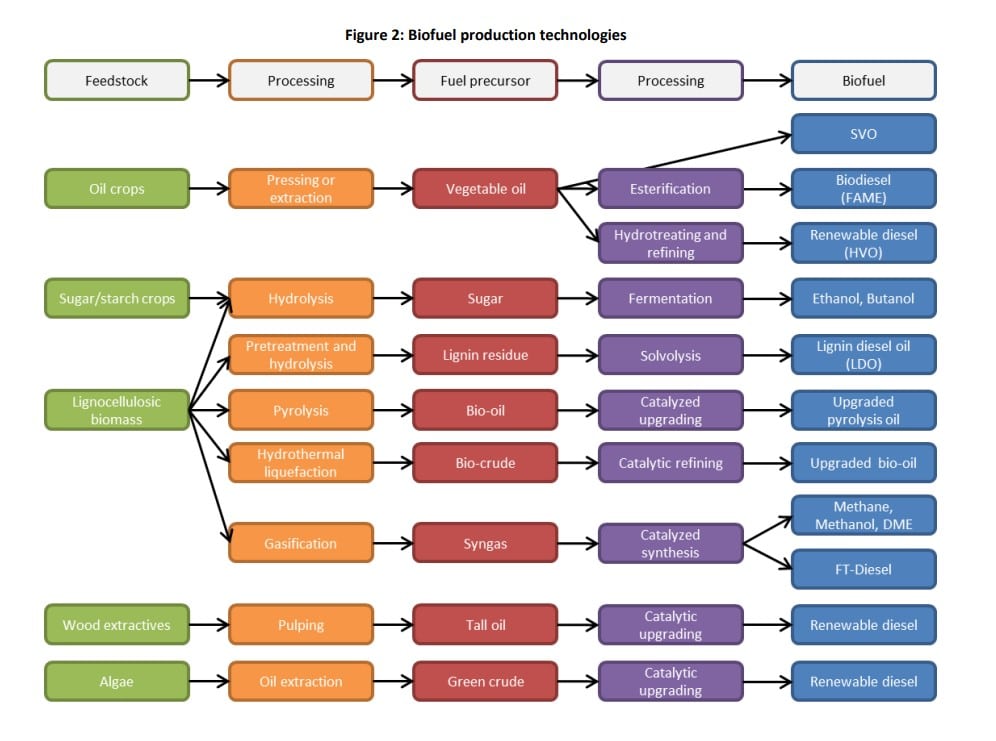
Source: https://www.etipbioenergy.eu/
How do biofuels work?
Biofuels, depending on their type and consistency, are combusted in engines to produce energy. They essentially work as substitutes or additives to conventional fuels, providing the necessary power to propel vehicles, including marine vessels. Modern merchant ships are usually powered by two-stroke or four-stroke diesel engines using traditional fuels such as heavy fuel oil (HFO), marine diesel oil (MDO), and low sulfur heavy fuel oil (LSHFO). The unique feature of biofuels is their ‘drop-in’ capability, which allows them to replace or mix with traditional fuels without major modifications to the existing infrastructure.
Benefits of implementing biofuels
- Reduction in GHG Emissions: One of the standout advantages of biofuels is their potential to reduce carbon output. If produced sustainably, biofuels can significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional fossil fuels.
- Immediate Integration: The ‘drop-in’ characteristic of biofuels makes them particularly appealing. They can seamlessly integrate into the current marine system without the need for substantial modifications to engines, fuel tanks, or supply systems.
- Emission Control: Biofuels contain negligible sulfur. Hence, they could be a go-to solution for ships operating in Emission Control Areas (ECAs), where strict emission standards are in place.
- Diverse Production Methods: Various biofuel production technologies, from diesel-type hydrocarbons for diesel engines to ethanol and methanol for spark ignition engines, provide multiple avenues for biofuel application in marine engines.
- Support for Climate Goals: Adopting biofuels can significantly contribute to the GHG-reduction ambitions set by the EU and the International Maritime Organization (IMO) for the maritime industry.
Read more: How Ship Fuel Efficiency Impacts the Maritime Industry
Challenges of biofuels
However, the adoption of biofuels in the maritime sector isn’t without its challenges:
- Cost: Biofuels generally cost more than conventional marine fuels, which can be a deterrent to their widespread adoption.
- Logistic Support: Not all ports are equipped to handle biofuels, especially those not compatible with diesel-type fuels. This can lead to logistical challenges for ships relying on biofuels.
- Expertise: The marine sector currently lacks comprehensive expertise in handling some biofuels, including understanding their long-term stability.
- Fuel Test Data: For broader acceptance, there’s a need for long-term fuel test data to ensure the fuel’s safety and reliability.
- Space Considerations: Some biofuels, such as methanol and gaseous fuels, are less energy-dense, which might require more storage space, thereby reducing cargo space on vessels.
- Safety: Using certain biofuels, like methanol or gaseous fuels, might come with specific safety requirements.
How data can support the implementation and management of Marine Biofuels
When implementing and monitoring biofuels in the maritime sector, the significance of data management becomes even more pronounced. Here’s a look at the role of data management in the maritime biofuel journey:
- Tracking Emissions: One of the primary goals of shifting to biofuels is reducing GHG emissions. Efficient data management systems can accurately monitor and record emissions from vessels using biofuels, offering real-time insights and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
- Operational Efficiency: By collecting and analyzing data related to the combustion of biofuels, maritime operators can optimize engine performance, adjust fuel mixtures, and ensure the efficient use of biofuels. This is vital, especially given the varying characteristics of different biofuels.
- Safety Monitoring: Biofuels, especially the newer or less common variants, require stringent safety measures. Data management systems can monitor storage conditions, fuel stability over time, and other safety metrics, promptly flagging potential issues.
- Research & Development: As the maritime industry experiments with different types of biofuels, collecting and analyzing data on their performance, emissions, and compatibility can drive further research. This data-centric approach can lead to the development of more efficient and sustainable biofuel variants.
- Regulatory Compliance & Reporting: With regulations like the IMO DCS, EEXI, CII and the EU-MRV/ETS in place, maritime operators must report their fuel consumption and emissions. Effective data management systems simplify this process, automating reporting and ensuring compliance with international standards. New fuels will require adapting calculations.
- Stakeholder Communication: Transparent data management allows operators to share their sustainability achievements with stakeholders. Whether it’s shareholders, clients, or regulatory bodies, providing data-backed insights on biofuel adoption and its benefits fosters trust and encourages broader industry participation.
Read more: The Potential of Data Sharing in the Maritime Industry
Conclusion
As the world seeks sustainable alternatives to counter the climate crisis, biofuels emerge as a promising solution. Their potential to reduce carbon emissions and integrate seamlessly into the existing infrastructure is commendable. However, their broader adoption requires addressing challenges related to cost, logistics, expertise, and safety. With the right investments and a collaborative approach between policymakers, researchers, and industry stakeholders, biofuels can undoubtedly pave the way for a greener maritime future.

